Lake Victoria is a monumental feature of the African continent, a vast inland sea so large that it influences the weather of the regions surrounding it. As Africa’s largest lake by area and the world’s largest tropical lake, its scale is immense. Shared by three nations—Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania—it is not a typical safari destination filled with game-viewing vehicles, but rather the heart of a vibrant region where millions of people depend on its rich fisheries. The lake is the source of the White Nile, a fact that fascinated and drove 19th-century European explorers on epic quests. Dotted with thousands of islands, including the culturally unique Ssese Islands, and surrounded by bustling towns and fishing villages, Lake Victoria offers a look into the lifeblood of East Africa, a place of immense ecological importance, cultural richness, and natural power.
Listen to an introduction about Lake Victoria
![]()
Name and Location
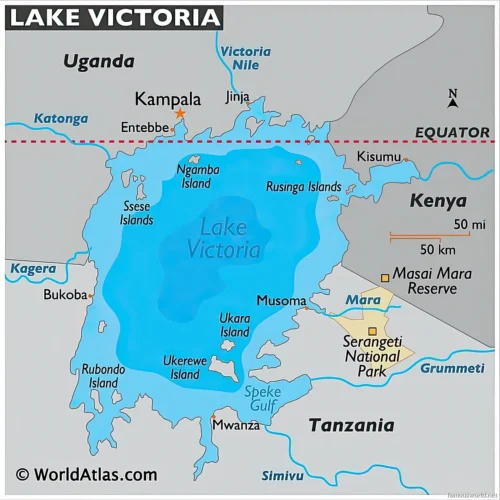
- Name: Lake Victoria (also known as Nam Lolwe in Luo; ‘Nnalubaale in Luganda; Nyanza in some Bantu languages).
- Location: East-Central Africa, with its shores divided among Tanzania (49%), Uganda (45%), and Kenya (6%).
How to Get There
Access to the lake depends on the country and the specific destination along its vast shoreline.
- Kenya: The main port city is Kisumu, which has an international airport (KIS) with flights from Nairobi and other regional hubs.
- Uganda: The primary access points are Entebbe, home to Uganda’s main international airport (EBB), and the port city of Jinja. Ferries and boats depart from these areas to the Ssese Islands and other destinations.
- Tanzania: The major port cities are Mwanza, which has an airport (MWZ), and Bukoba. These serve as gateways to the Tanzanian side of the lake and its islands, like Rubondo Island National Park.
Landscape and Ecosystems
The lake is a massive, relatively shallow freshwater body with a diverse and challenged ecosystem.
- Vast Freshwater Sea: The most defining feature is its sheer size. It often feels like an ocean, with a horizon that meets the water and localized storms that can create rough conditions.
- Archipelagos and Islands: The lake is dotted with numerous islands, ranging from small, uninhabited rocky outcrops to large, populated archipelagos like the Ssese Islands in Uganda and Ukerewe Island in Tanzania. These islands often have lush tropical vegetation and their own unique microcultures.
- Wetlands and Shorelines: The lake’s shores are lined with extensive papyrus swamps and wetlands, which are critical habitats for birdlife, including the iconic Shoebill. The shoreline varies from bustling cities and fishing villages to quiet, rural landscapes.
- Ecological Challenges: The lake’s ecosystem has faced significant challenges, including the introduction of invasive species like the Nile perch and water hyacinth, pollution, and overfishing, which have had a major impact on its native biodiversity.
What Makes It Famous
Lake Victoria’s fame is tied to its immense scale, its role in history, and its ecological significance.
- Africa’s Largest Lake: Its status as the continent’s largest lake makes it a major geographical feature of the planet.
- Source of the White Nile: It is famously recognized as the primary reservoir for the White Nile, a geographical puzzle that drove intense exploration in the 19th century and was a key goal in the “Scramble for Africa.”
- Rich Biodiversity: Despite challenges, the lake and its surrounding wetlands support a huge diversity of wildlife, especially birds, hippos, and crocodiles. It was once home to an incredible radiation of several hundred species of cichlid fish found nowhere else on earth, though many are now extinct.
- Economic Heartland: The lake supports one of the largest freshwater fisheries in the world, providing a livelihood for millions of people in the surrounding countries.
Differences from Other Wonders
The vast, life-sustaining freshwater ecosystem of Lake Victoria is profoundly different from the tropical, saline, and historical environment of Zanzibar.
- Environment (Freshwater Inland Sea vs. Saltwater Archipelago): Lake Victoria is a massive freshwater lake. Zanzibar is an archipelago in the saltwater of the Indian Ocean.
- Core Story (Natural Resource and Lifeblood vs. Cultural and Trade Crossroads): Lake Victoria’s story is centered on its role as a vital natural resource—a source of water, food, and transport for millions. Zanzibar’s story is one of human history, as a center for the spice trade, slavery, and the fusion of global cultures.
- Primary Attraction (Local Life and Nature vs. History and Beaches): The main attractions of Lake Victoria are experiencing its scale, visiting island communities, and birdwatching in its wetlands. Zanzibar’s primary attractions are the historic Stone Town and its world-famous white-sand beaches.
- Atmosphere (Working and Powerful vs. Touristic and Tropical): Lake Victoria feels like a powerful, working body of water, central to the economy and daily life of the region. Zanzibar has a more developed tourism infrastructure and a classic tropical island holiday atmosphere.
Location on world map